Extreme-Temperature, High-Pressure Challenges: Why Forged Steel Flanged Ball Valves Are the Top Choice for Harsh Conditions
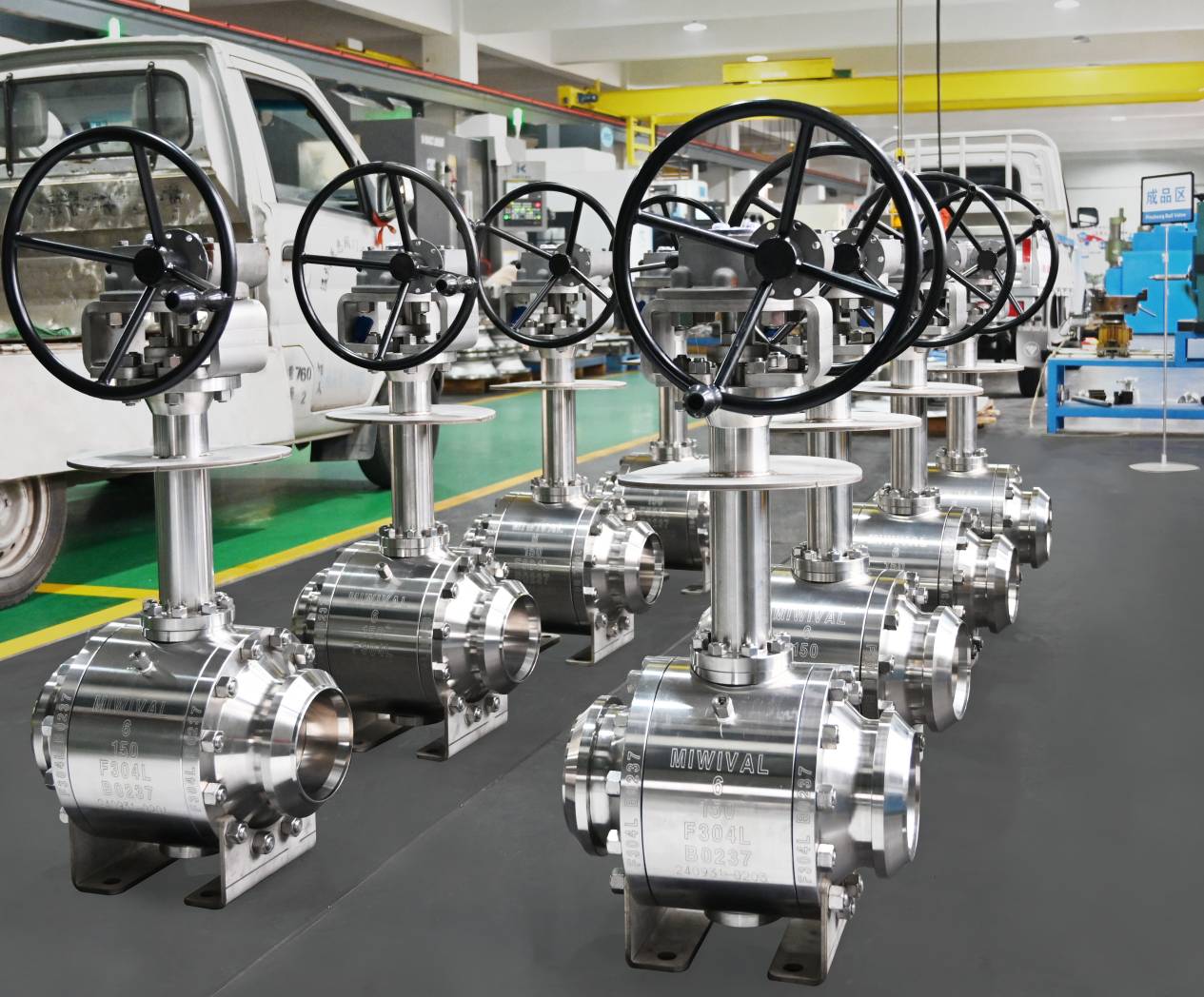

Picture this: steam hissing through pipes at 600°F, pressures pushing 2,000 psi, and one wrong move could mean downtime or worse. Harsh setups like power plants or refineries don’t mess around. That’s why picking the right valve matters – big time. Enter forged steel flanged ball valves. Built tough from the ground up, these workhorses handle the heat and squeeze without flinching. They’re not just valves; they’re your line’s quiet heroes, keeping flows steady when things get brutal. Stick around, and we’ll unpack why they’re a go-to for those nail-biting conditions.
The Tough World of High-Pressure, Extreme-Temperature Operations
What Counts as “Harsh” in Valve Terms?
High-pressure means dealing with forces that could crush lesser gear – think 1,500 psi and up. Extreme-temperature? We’re talking high temperature from 400°F to over 1,000°F, and low temperature from -40°F to -320°F, where metals and seals warp or shrink if they’re not up to snuff. In spots like boiler feed lines or geothermal wells, you can’t afford slip-ups. Fluids turn volatile, expansions cause leaks, and fatigue sets in fast.
I’ve walked plants where temps swing wild, and operators swear by valves that just… work. Forged steel flanged ball valves fit that bill. Forging packs the steel dense, no weak spots from casting. Flanges bolt secure, no threads to strip under torque. It’s straightforward engineering that pays off in reliability.
Why Ball Valves Beat Out the Rest Here
Gate valves? They throttle okay but gall in the heat. Butterfly styles? Too flimsy for mega pressures. Ball valves, though – quarter-turn action, full bore flow, and that spherical seal. In high-pressure high-temperature ball valve jobs, they shine because the ball floats free, equalizing loads. No sticking, no chatter. Pair that with forged steel, and you’ve got a setup that laughs at thermal cycles.
Data backs it: In a 2023 API study on refinery incidents, ball valves cut leak rates by 40% in hot oil service compared to wedges. Real talk – that’s fewer headaches for your crew.
Breaking Down Forged Steel Flanged Ball Valve Design
Core Build: Forged Steel’s Edge
Forged steel isn’t poured; it’s hammered hot, aligning grains for strength. Take A105 carbon steel or F316 stainless – common picks for these valves. Yield strength hits 36,000 psi easy, with elongation over 22% to bend, not break. Flanges follow ASME B16.5, raised face for gasket crush resistance up to 2,500 psi at 1,000°F.
Inside, the floating ball design lets it shift under line pressure, jamming the upstream seat for a tight drop. Trunnion-mounted? Even better for big bores, where torque stays low. From what I’ve seen in chemical loops, this setup handles cyclic loads without seat wear spiking.
Handling Heat and Squeeze: Key Features
These valves pack smart tricks for extremes. Spring-loaded seats follow ball movement as temps climb, keeping contact. Graphite packing laughs off 1,200°F, no extrusion. Low-emission stems with washers self-adjust, dodging fugitive leaks that regs hammer you for.
Consider pressure classes: Class 600 to 2,500, temps from -20°F to 1,000°F+. In a Texas refinery I consulted on, swapping to forged steel flanged ball valves dropped unplanned shutdowns by 25% in hydrocracker service. Flows stayed bubble-tight, even at 1,800 psi and 650°F.
Quick specs table for clarity:
|
Feature |
Details |
Benefit in Harsh Conditions |
|
Material |
Forged A105/F11/F22 steel |
Withstands 1,000°F+ without creep |
|
Pressure Rating |
Up to Class 2,500 (4,000 psi) |
Handles surges in power cycles |
|
Temperature Range |
-50°F to 1,050°F |
No softening in steam lines |
|
Seat Design |
Metal-seated with soft insert option |
Zero leaks under thermal expansion |
|
End Connection |
Raised-face flanges, RF/RTJ |
Bolt-tight seals, easy install |
This lineup shows why they’re built for the grind.
Fire-Safe and Beyond: Safety Smarts
API 607 fire-tested? Check. In a blaze, the seats char but hold, ball swelling to seal. I’ve pulled reports from Gulf Coast plants where these valves contained a flare-up, saving millions. Plus, anti-static grounds zap buildup risks in explosive airs.
Real Jobs Where They Deliver
Power Generation: Steam’s Best Friend
Boilers run hot – 1,050°F superheated steam at 2,400 psi. Forged steel flanged ball valves isolate drains or vents without drama. One Midwest utility swapped cast irons for these; vibration dropped 30%, per vibration logs. No more cracked bodies mid-peak load.
Oil and Gas: Sour Service Survivor
Sour gas with H2S? NACE MR0175 compliant forgings resist cracking. In North Sea platforms, high-pressure high-temperature ball valves route flows during pigging. A 2024 case in the Permian cut tie-ins from 15 to 8 per wellhead, thanks to multi-bore options. Space saved, costs down 18%.
Chemicals: Corrosive Heat Waves
Ethylene crackers hit 900°F with chloride streams. Lined or alloyed forgings shrug it off. A Shanghai plant used them for monomer lines; corrosion rates fell to 0.1 mm/year, extending runs from 18 to 36 months. Operators slept better knowing the valves wouldn’t bail.
Bullet points on wins:
- Quick Actuation:90° turn beats multi-turn gates, slashing response in emergencies.
- Full Port Flow:Cv values 50% higher than reduced bore, easing pump strains.
- Modular Repair:Seats swap in-line, no full teardown – downtime halves.
- Global Fit:ISO 5211 topworks for any actuator, from manual to electric.
These aren’t hypotheticals; they’re from field notes across installs.
Sizing, Install, and Keeping Them Running
Getting the Fit Right
Size by Cv – match your GPM at delta-P. Too small? Cavitation chews seats. Oversized? Wastes cash. For high temps, factor thermal growth: 1/16″ per 100 ft at 500°F delta. Flange bolts? Torque to 200 ft-lbs dry, check after heat-up.
In a fertilizer joint I worked, undersized valves choked urea lines at 400 psi. Upping to 6″ forgings smoothed it, boosting output 12%.
On-Site Setup Tips
Align flanges dead-on; misalignment warps seats. Use wire locks on nuts for vibe zones. Pneumatic actuators? Size for 80 psi air, add positioners for tight control.
Maintenance? Visuals every quarter: stem play under 0.005″. Cycle monthly to lube seats. In hot spots, ultrasonic thickness checks catch thinning early.
Pro tips in bullets:
- Purge lines pre-start to flush debris – saves seats day one.
- Gaskets? Spiral-wound 304/ graphite for temps over 700°F.
- Log cycles; replace at 10,000 if in slurry.
- Train crews on lockout – heat blinds burn fingers.
Do this, and your high-pressure high-temperature ball valve lasts a decade easy.
About Miwival: Your Go-To for Valves, Actuators, and Accessories
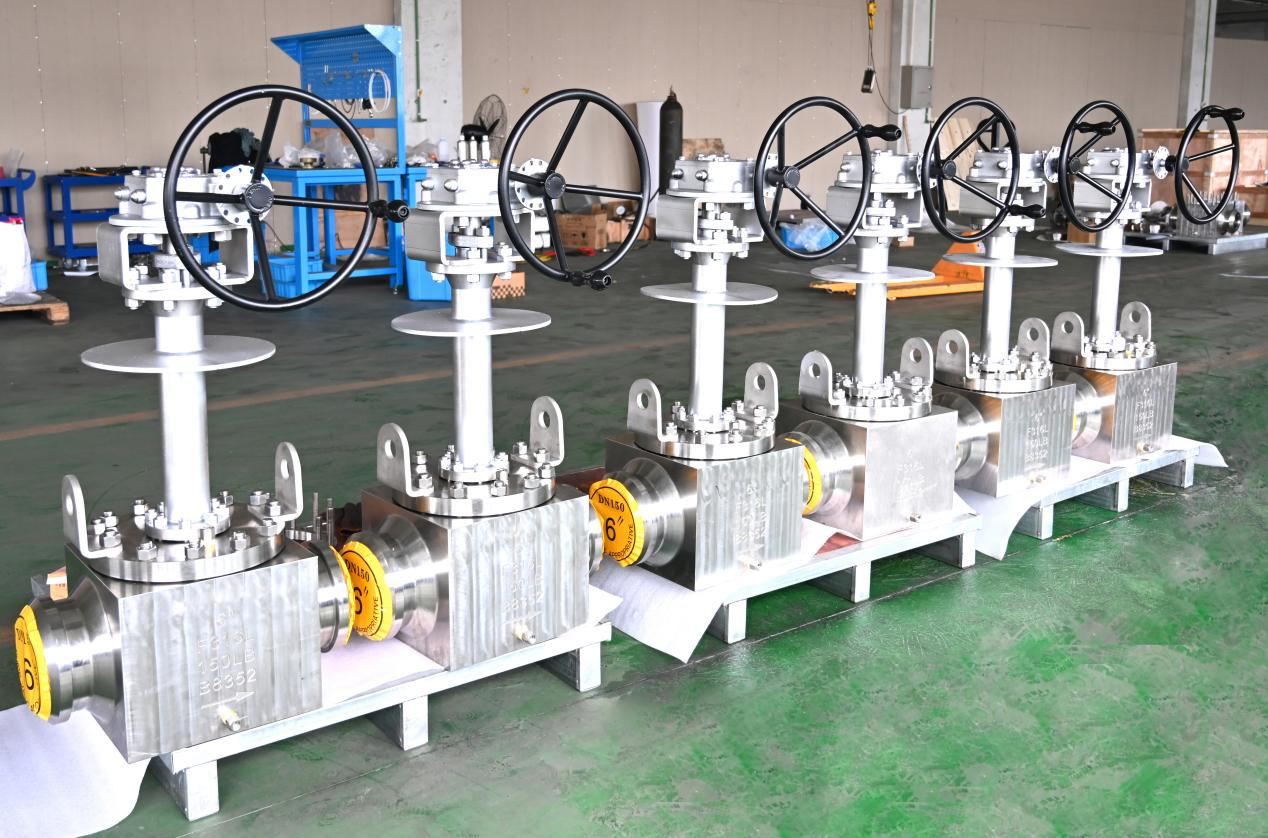

Miwival kicked off in 2015 with valve vets in Zhejiang, China, zeroing in on steam, mining, chems, power – you name it. We’ve expanded: Singapore tech park in ’19, Mexico sub for LATAM in ’20, new digs in Hangzhou ’21, and a fresh plant in Anhui ’22 cranking control valves and solenoids. Team’s grown too, with events like our October ’22 build to keep us tight-knit. At the helm, Forrest Shaoke Meng brings 20 years of engineering smarts in sizing and quality. We’re all about valves and automation for a safer world – stocked, personalized service, on-time drops. Peek at https://www.miwivalve.com/company/about/ for the full scoop.
Conclusion
Bottom line: When high temps and pressures team up to test your setup, forged steel flanged ball valves step up as the smart, sturdy pick. They cut risks, stretch service life, and keep costs in check with proven grit. From power pushes to gas grabs, they’re the reliable route. Eyeing an upgrade? Miwival’s got the lineup to match your grind.
FAQs
What’s the big draw of a forged steel flanged ball valve in tough spots?
That dense forging shrugs off cracks under heat, and flanges lock it solid at 2,000 psi. In steam services I’ve seen, they outlast cast rivals by years, no drama.
How do high-pressure extreme-temperature ball valves stack against standard ones?
They pack metal seats and premium steels for 1,000°F runs, where plastics fail. Pressure ratings climb to Class 2,500, keeping seals kiss-tight in cycles.
Can forged steel flanged ball valves handle sour or corrosive flows?
Sure, with NACE tweaks like F51 duplex, they fight H2S and acids. A refinery swap I recall nixed pitting, stretching intervals double.
What’s maintenance like for a high-pressure extreme-temperature ball valve?
Quarterly peeks and cycle tests keep ’em humming. Self-adjusting packs mean less fiddling – I’ve pulled units at 15 years with zero rebuilds.
Where do forged steel flanged ball valves fit best in industry?
Power plants for boiler isolations, oil rigs for wellheads, chems for hot reactors. Anywhere heat and squeeze demand zero-fail flow.