Extreme Temperature Challenges Control Valve Solutions for Cryogenic and High-Heat Processes

Industrial work can really test gear to the breaking point. Picture dealing with liquefied natural gas that dips way down to -196°C. Or handling superhot steam in a power plant furnace that climbs to 650°C. In those situations, a regular control valve simply won’t hold up. It might leak, cause shutdowns, or even create serious safety problems. Nobody wants that.
Specialized control valves come to the rescue here. They manage flow just right. And they tough it out through those wild temperature changes. Folks in oil and gas, petrochemicals, power plants, and chemical facilities count on them every day. These valves keep things running steady. They cut down on wasted energy. Plus, they make the whole setup more dependable.
Understanding the Challenges in Extreme Temperatures
Harsh conditions hit control valves pretty bad. Metals shrink or swell in uneven ways. Seals wear out fast. And keeping the position exact becomes a real struggle.
Cryogenic Conditions: The Deep Freeze
In cold applications, like LNG terminals or plants that separate air, fluids get super chilly. They often hit around -196°C for stuff like liquid nitrogen or oxygen.
Typical troubles pop up, such as:
- Metals getting brittle: Lots of steels turn fragile in the freeze. They can crack under stress.
- Seals breaking down: Regular rubber-like materials stiffen up. Then they leak precious or dangerous gases.
- Parts shrinking differently: Things contract at odd rates. That puts strain on stems and tops.
- Frost building up: Any moisture freezes solid. It can jam movers or stuffing.
Take a true story from an LNG unloading job. Bad valve performance led to a partial halt. Tankers waited longer. Losses piled up into millions. Good control valves stop those messes cold.
High-Heat Environments: The Intense Burn
On the other hand, hot processes expose valves to blazing temps. Think steam lines in refineries or feeds in steel mill furnaces. Heat can reach 650°C or higher.
Main issues include:
- Parts expanding too much: Things grow at different speeds. Seats warp. Stems get stuck.
- Materials wearing away: Rust-like oxidation or slow creep weakens bodies over years.
- Seals failing quick: Heat destroys packing. Emissions sneak out.
- Damage from flashing steam: Sudden vapor can pit insides fast.
In power stations, uneven steam control has caused boilers to run poorly. Fuel costs jumped 5-10% in some cases.
Power Plant Valves and Solutions | THINKTANK
|
Challenge |
Cryogenic (-196°C) |
High-Heat (up to 650°C) |
|
Primary Risk |
Brittleness and shrinkage |
Swelling and rusting |
|
Common Failure |
Leaks from stiff seals |
Stuck stems or worn seats |
|
Industry Example |
LNG storage/transfer |
Superhot steam in turbines |
|
Impact |
Safety issues, lost product |
Lower efficiency, bigger bills |
Key Features of Effective Control Valves for Extremes
Today’s control valves fight these problems with clever builds.
Materials That Stand Strong
- Tough stainless steels, like CF8M, stay flexible even in deep cold. They don’t crack easy.
- Strong alloy steels, such as WC6 or WC9, fight off creep and rust in fierce heat.
- Long bonnets in cold jobs keep packing cozy. No freezing there.
Trim and Seating Designs
- Step-by-step trims ease pressure drops slowly. That cuts noise and wear in hot steam.
- Guided cages or holder-style plugs keep things steady over big temp shifts.
- Special bellows seals block leaks completely in tricky areas.
Flow Characteristics
Choices like equal percentage or straight-line flow fit the job. Equal percentage shines for changing loads. It gives fine tuning when barely open.
Actuation Options
Air-powered diaphragms, cylinders, or electric ones pair up nicely. They respond sharp, even in rough spots.
All this leads to valves with great range—often 50:1 or more. So they handle tiny trickles or full blasts without missing a beat.
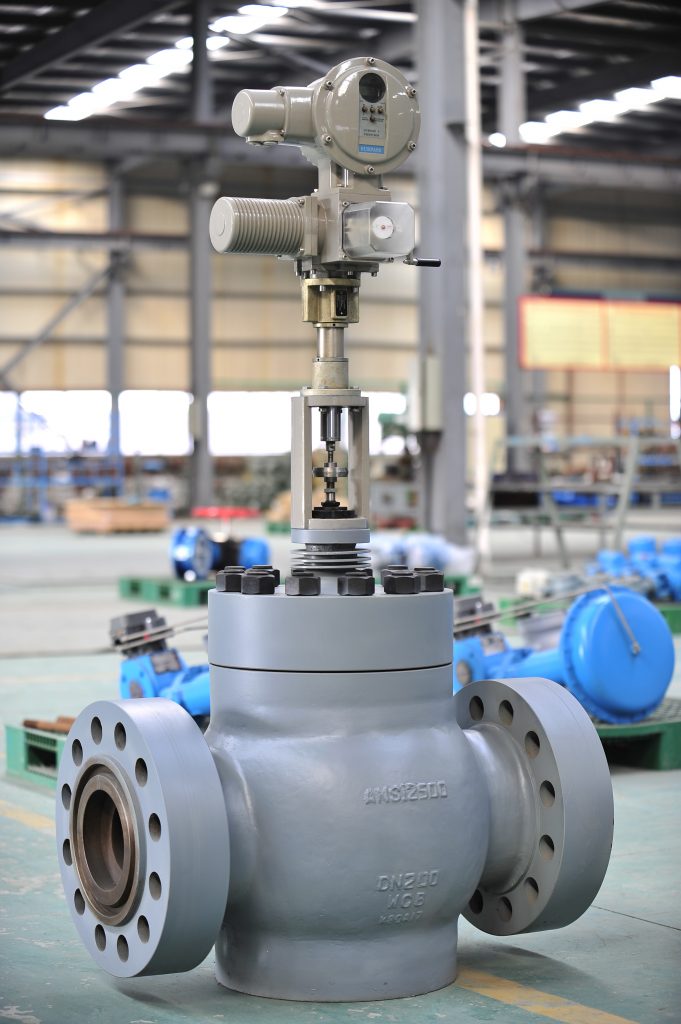
Globe Control Valves: A Versatile Choice for Tough Duties
Globe-style control valves really stand out in harsh temp work. Their round body routes flow through swapable insides. That allows top-notch throttling.
Why they work so well:
- Broad temp handling: Many cover -196°C to 650°C without a hitch.
- Easy-to-build modular: Change trims quick for fixes. No fancy tools.
- Solid shutoff: Tight clamping seats seal firm.
- Field-tested everywhere: Plants around the globe use them for steam, gases, and liquids in hard service.
In chemical plants, these valves meter cold feeds precisely. They avoid over-chilling that could clog pipes. In power setups, they direct high-pressure steam. Turbines stay efficient that way.
The Benefits of Using Globe Valves in Fluid Control Systems – Indusrtrial Valve Manufacturer
About Miwival: Your Trusted Valves, Actuators, and Accessories Supplier

Miwival has built a solid rep as a reliable source for valves, actuators, and accessories in flow management. They stress quality from start to finish. That means dependable products for fields like power, chemicals, oil and gas, and others. Their range features strong globe control valves made for rough duty. Automation add-ons focus on safety and saving money. Quick stock, fast shipping, and knowledgeable help make them a great go-to for challenging jobs.
Conclusion
Dealing with wild temperatures doesn’t need to bring constant headaches about valve breakdowns. Pick the proper control valve, and tough spots turn into smooth runs. It stops leaks in cold lines. It fine-tunes steam in hot ones. Safety improves. Uptime grows. Costs drop in the end. Managers and engineers see the payoff quick—usually from less fixing and lower energy bills.
Frequently Asked Questions
What temperature range can a typical control valve handle in cryogenic applications?
Plenty of solid control valves go as low as -196°C. That’s perfect for liquids like nitrogen or oxygen. It keeps materials tough and seals snug all the way.
How do control valves perform in high-heat steam processes?
They take up to 650°C no problem. Heat-tough materials and smart designs fight swelling and wear. Step trims manage pressure drops well in steam.
Why choose globe-style control valves for extreme conditions?
Their swap-friendly build, accurate flow patterns, and simple upkeep make them flexible. They deliver precision and strength in both freezing and scorching setups.
What materials are best for control valves in temperature extremes?
Tough stainless steels do great in cold. Alloy steels manage heat fine. These picks hold up strong and resist breakdown long-term.
Can control valves reduce costs in tough processes?
Absolutely. Sharper control trims energy waste. It cuts stops. Equipment lasts longer. Many operations have seen clear drops in running costs.