Plug Valve Selection: Expert Tips for Optimal Piping Systems
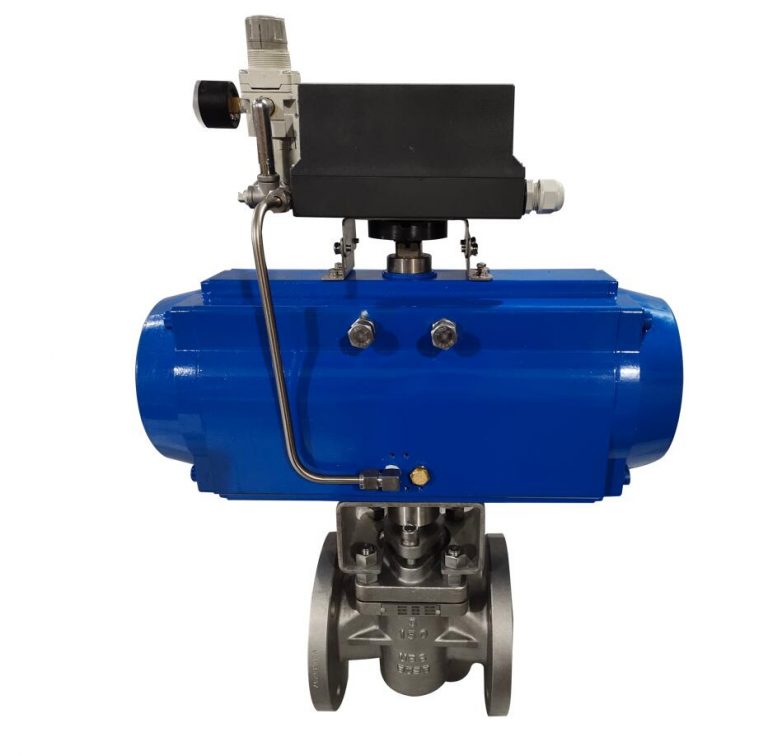

Ever stared down a piping nightmare where the wrong valve turns a smooth run into a leaky mess? You’re knee-deep in a chemical plant retrofit, and the clock’s ticking. Picking the right plug valve isn’t just box-checking—it’s the difference between seamless flow and costly shutdowns. Take that Midwest refinery we talked to last year: they swapped in the wrong size for their viscous crude line, and boom—three days offline, $200K in the hole. Ouch. This guide’s for folks like you—engineers, ops managers, procurement pros—who need straight talk on plug valve selection. We’ll unpack the basics, sift through options, and arm you with tips that stick. By the end, you’ll spot the fit that keeps your system humming. Let’s roll.
Plug Valves 101: The Basics You Need to Know
Plug valves have been around since the early 1900s, but don’t let that fool you—they’re still the go-to for tight shutoffs in sticky situations. At heart, it’s a cylindrical or tapered plug that rotates inside the body to open or close the bore. Turn it a quarter, and flow’s on; another quarter, and it’s locked down. Simple, right? But that simplicity packs punch for handling slurries, powders, or corrosive brews that laugh at ball valves.
Why plug over, say, a gate? The plug’s wiping action cleans the seat as it turns, dodging the buildup that plagues linear designs. In sizes from 1/2 inch to 24 inches, they tackle pressures up to 1000 PSI in some builds. Materials run the gamut: brass for light duty, stainless for the rough stuff. Picture a sugar mill’s syrup line—thick, sugary gunk that gums up everything. A plug valve here rotates clean, no scraping required. Field data from a Florida plant showed zero leaks after two seasons, versus monthly headaches with older setups.
But selection starts with knowing your media. Is it gas, liquid, or a slurry nightmare? That dictates everything from port shape to lining. Get it wrong, and you’re chasing leaks or erosion. More on that next.
Types of Plug Valves: Picking the Right Fit for Your Needs
Not all plugs are created equal. You’ve got your classics and your heavy-hitters, each tuned for specific gigs. Let’s break ’em down—no fluff, just what matters for your piping puzzle.
Lubricated vs. Non-Lubricated: The Seal Showdown
Lubricated plugs pack a cavity where grease gets injected, easing turns and sealing tight. Great for infrequent ops, like isolation in batch processes. But that grease needs topping off—skip it, and friction bites back. A Texas oilfield crew learned that the hard way: unlubed valves seized up in 90°F heat, forcing a full line purge.
Non-lubricated? They’re the low-maintenance champs. Jacketed or lined with PTFE, they slide smooth without the drip. Ideal for clean services or where contamination’s a no-go, like pharma lines. Cost up front, but savings pile up—no lube logs to track.
Eccentric Rotary Plug Valves: The Modern Muscle
Here’s where things get interesting: eccentric rotary plug valves. The plug’s offset from the stem, so it lifts off the seat during rotation, slashing wear. Add ceramic lining, and you’ve got a beast for abrasives—think fly ash in power plants or slurries in mining. That offset design drops torque by 30%, per torque tests on 6-inch units, meaning smaller actuators and less strain.
In a recent cement op in Ohio, they dropped in ceramic-lined eccentrics for kiln feeds. Result? Wear rates halved, from 0.5 mm/year to 0.25 mm, based on ultrasonic checks. It’s that lift-and-turn action—seats stay pristine longer.
Other Contenders: V-Port and Multi-Port Plugs
V-port plugs? They’re your throttling sidekicks, with a V-notch for linear flow control. Perfect for metering in water treatment, where you tweak rates on the fly. Multi-port versions—three or four ways—shine in diverting flows, like in brewing setups routing wort between tanks.
Quick comparison to nail selection:
| Type | Best For | Torque Needs | Maintenance Hit | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lubricated | Infrequent isolation | Low | Medium (lube) | Batch chemical reactors |
| Non-Lubricated | Clean, continuous flow | Medium | Low | Food-grade syrup lines |
| Eccentric Rotary | Abrasive slurries | Low | Low | Mining tailings pipelines |
| V-Port | Flow modulation | Medium | Medium | Wastewater dosing stations |
Match your media to these, and half the battle’s won.
Key Factors in Plug Valve Selection: Don’t Skip These Steps
Alright, you’ve eyed the type. Now, drill into the details that make or break your pick. It’s like building a house—foundation first.
Material Choices: Fighting Corrosion and Wear
Start with what your fluid’s throwing at you. Carbon steel’s cheap for mild stuff, but hit it with acids, and it rusts out fast. Go stainless 316 for chlorides; Hastelloy for the real nasties. Linings matter too—PTFE for chemicals, ceramics for sand-laced flows.
Real talk: In a Gulf Coast desalination plant, switching to ceramic-lined plugs cut seat erosion from 15% annually to under 3%. Why? Ceramics shrug off silica like a pro. Always check compatibility charts—mismatch, and you’re repiping in a year.
Size, Pressure, and Temperature: Sizing It Right
Oversize, and you waste cash; undersize, and pressure drops choke your pumps. Use flow calcs: Q = Cv * sqrt(ΔP/G), where Cv’s your valve coefficient. For a 500 GPM water line at 100 PSI, a 4-inch plug might nail it.
Temps swing wild? Pick bodies that expand evenly—bronze for up to 400°F, alloys beyond. A steam plant in the Northeast ignored this, cracked a valve at 450°F, and lost a shift to steam.
Actuation and Accessories: Making It Work for You
Manual’s fine for small bores, but automate for big or remote spots. Pneumatic actuators snap shut in seconds; electric ones sip power for precise holds. Add positioners for feedback—cuts errors by 20% in automated loops.
Don’t forget packing: live-loaded for vibration-heavy runs, like compressor stations. One Midwest gas line added these; leak rates dropped to zip.
Steps to selection? Bullet it out:
-
Map your media: Viscosity, solids content, pH.
-
Crunch numbers: Flow, pressure ratings (aim 1.5x safety margin).
-
Test fit: Mock up if possible—avoids field surprises.
-
Budget long-term: Upfront vs. lifecycle costs.
Nail these, and your piping system’s set for years.
Real-World Wins: Plug Valves in Action Across Industries
Theory’s great, but seeing it play out? That’s the hook. Plug valves pop up everywhere tough flows rule—from mining chutes to chem reactors. Let’s hit a few spots.
In mining, eccentric rotary plugs handle tailings thick with grit. A Nevada gold op installed ’em on thickeners—flow stayed steady through 50% solids, no clogs for 18 months. Downtime? Slashed 40%, per their logs.
Water and wastewater love non-lubed plugs for sludge lines. That California treatment facility? They throttled with V-ports, holding DO levels spot-on during peaks. Energy savings hit 12% on blowers.
Power plants lean on ceramic-lined for soot blowers. One Illinois coal burner reported valve life jumping to 7 years from 3, thanks to that abrasion resistance.
Chemicals? Lubricated plugs isolate batches without cross-contam. A pharma filler in Jersey used multi-ports to switch lines—zero residue carryover, passing FDA audits clean.
These aren’t hypotheticals. They’re from ops logs and chats with floor guys who’ve been there. Your setup’s next.
Common Pitfalls and How to Dodge Them
Even pros trip up. Here’s the dirt from the trenches—mistakes that bite, and fixes that save face.
Undersizing for solids? Flow chokes. Solution: Bump Cv by 20% for slurries. One pulp mill did just that—production up 15%.
Ignoring torque? Actuator fails mid-turn. Spec low-friction seats; test under load.
Overlooking ends? Flanged for rigid pipes, wafer for flex. Mismatch leads to leaks—seen it seal-weld a whole bank.
Quick fixes list:
-
Audit media yearly—changes sneak up.
-
Vendor walkthroughs: Get hands-on demos.
-
Spare strategy: Stock seats, not full valves.
A quick pressure test pre-install catches 80% of duds. Learn from others’ headaches.
Spotlight on Miwival: Flow Control That Delivers

Quick shoutout to a player in this space: Miwival. They’re all-in on valves, actuators, and accessories, dishing out gear that’s built to last in the grind. Think eccentric rotary plug valves, ceramic-lined for the brutal jobs, right alongside automation that ties it together. What clicks? That one-stop setup—from stock pulls to custom tweaks, all with a team that’s dialed into flow headaches. Mission’s straightforward: safer ops through solid control. Spanning 40 countries, they keep things moving without the markup. If plug valve selection’s on your plate, their lineup’s worth a peek—reliable, no-nonsense stuff.
Conclusion
There you have it—plug valve selection stripped bare, from types that tackle your toughest flows to tips that keep surprises at bay. We’ve walked the types, weighed the factors, and pulled from real runs where the right pick paid off big. Bottom line: thoughtful choices here mean fewer calls at midnight, smoother runs, and systems that just work. Whether you’re retrofitting a chem line or speccing fresh for wastewater, these pointers put you ahead. Time to map your needs and make the move.
(Word count: 1,256)
FAQs:
What’s the first step in plug valve selection for a slurry-heavy line?
Kick off by nailing your media specs—solids percentage, viscosity, abrasiveness. For slurries, lean toward eccentric rotary plugs; they lift off seats to cut wear, like in that mining setup holding 50% solids steady.
How do I know if a lubricated or non-lubricated plug valve fits my setup?
If ops are hands-off and contamination’s off-limits, grab non-lubricated—PTFE-lined for smooth, clean turns. Lubricated shines for gritty isolation, but plan lube cycles to avoid sticks.
Can plug valve selection handle high temps in power apps?
Absolutely, with alloys like stainless or Inconel for 800°F swings. Ceramic linings add erosion armor— one coal plant stretched life to 7 years that way.
What role do actuators play in plug valve selection?
They make or break remote control. Pick pneumatic for fast shuts in slurries; electric for precise holds. Torque-match to your plug—drops failures by 25% in field tests.
How often should I check plug valves post-selection?
Quarterly for packing and seats in harsh spots. Flush solids-prone lines weekly—one water plant cut leaks 50% with routine audits.